The Powerful Truth Behind How GMO Seeds Shape Farmers’ Choices and Deepen Their Unseen Dependence on Seed Companies
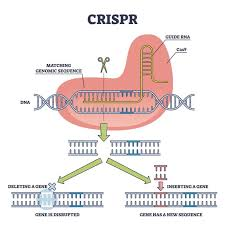
Introduction The adoption of genetically modified (GMO) seeds has introduced a transformative shift in agricultural production systems, influencing both technological adoption pathways and farmer-level decision-making. Historically, seed selection was governed by farmer-managed seed systems that promoted local adaptation, genetic diversity, and intergenerational knowledge transfer. However, the proliferation of patented GMO varieties—often marketed for traits such […]